The Importance Of Hpv Prevention
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection globally. It can lead to various types of cancers, such as cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the importance of HPV prevention and the measures that can be taken to reduce the transmission and risk of HPV-related diseases.
Vaccination is a key tool in HPV prevention. It is recommended for both males and females, ideally before they become sexually active. HPV vaccines have been proven to be highly effective in preventing infection with the most common types of HPV that cause cancer. By getting vaccinated, individuals can protect themselves from future HPV-related complications and reduce the spread of the virus to others.
Another important aspect of HPV prevention is promoting awareness and education. It is essential to inform the public, especially adolescents, about HPV, its transmission, and potential health risks. By raising awareness, individuals can make informed decisions about HPV vaccination, safe sex practices, and regular screening for HPV-related cancers.
Vaccination: Key Tool For Hpv Prevention
Vaccination is a key tool in the prevention of human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various types of cancer, including cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancer in females, and penile cancer in males. It can also cause anal and oropharyngeal cancers in both males and females. Vaccination against HPV has been proven to be highly effective in preventing these types of cancers.
There are currently three types of HPV vaccines available: Gardasil, Gardasil 9, and Cervarix. These vaccines protect against the most common types of HPV that cause cancer. Gardasil and Gardasil 9 also provide protection against genital warts, which are caused by certain types of HPV. The vaccines are administered through a series of injections, and the number of doses required varies depending on the age at which the vaccination is initiated.
The timing and dosage of HPV vaccination is an important factor in achieving optimal protection. The vaccines are recommended to be given before the onset of sexual activity, as they are most effective when administered to individuals who have not been exposed to HPV. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend routine HPV vaccination for both males and females at the age of 11 or 12. However, the vaccines can be given to individuals as young as 9 years old and up to the age of 45.
Types Of Hpv Vaccines Available
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various health complications, including genital warts and certain types of cancer. Fortunately, vaccines have been developed to prevent HPV infection and the associated diseases. There are currently three main types of HPV vaccines available:
1. Bivalent HPV vaccine: This vaccine protects against the two most common types of HPV, namely HPV-16 and HPV-18. These types are responsible for around 70% of cervical cancer cases. The bivalent HPV vaccine is primarily recommended for females between the ages of 9 and 25. It is administered in three doses over a span of six months.
2. Quadrivalent HPV vaccine: In addition to protecting against HPV-16 and HPV-18, the quadrivalent HPV vaccine also targets two other types of HPV, HPV-6 and HPV-11. These types are known to cause genital warts. The quadrivalent vaccine is suitable for both males and females between the ages of 9 and 45. Similar to the bivalent vaccine, it is administered in three doses over a period of six months.
3. Nonavalent HPV vaccine: The nonavalent HPV vaccine provides protection against nine different types of HPV, including those covered by the bivalent and quadrivalent vaccines. It also targets five additional high-risk types of HPV. This vaccine is recommended for both males and females aged 9 to 45. Like the other HPV vaccines, it is given in three doses over a period of six months.
- HPV vaccines have proven to be effective in preventing HPV infections and reducing the risk of associated diseases. It is important to note that these vaccines are most effective when given before a person becomes sexually active and exposed to HPV. It is essential to consult healthcare providers to determine the most suitable vaccine and vaccination schedule based on individual circumstances and age.
| HPV Vaccine | Target HPV Types | Suitable for | Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalent | HPV-16, HPV-18 | Females aged 9-25 | Three doses over six months |
| Quadrivalent | HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-6, HPV-11 | Males and females aged 9-45 | Three doses over six months |
| Nonavalent | HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-6, HPV-11, and others | Males and females aged 9-45 | Three doses over six months |
Timing And Dosage Of Hpv Vaccination
When it comes to protecting oneself against Human Papillomavirus (HPV), vaccination plays a crucial role. But it’s not just about getting vaccinated; the timing and dosage of the HPV vaccine are equally important factors. The HPV vaccine is typically recommended for both males and females starting as early as age 9, up until the age of 26. It is essential to follow the recommended vaccination schedule to ensure maximum efficacy and protection against HPV.
To understand the timing and dosage of HPV vaccination, it is crucial to know that the HPV vaccine is administered in a series of shots. For individuals aged 9 to 14, two doses of the vaccine are recommended, with the second shot given six to twelve months after the first dose. Adolescents and young adults aged 15 to 26, who did not receive the vaccine when they were younger, should ideally receive three doses. The second shot is given two months after the first dose, and the third shot completes the series at approximately six months following the initial dose.
It is important to adhere to the recommended timing of these doses to ensure optimal protection. Delaying or missing a dose can compromise the effectiveness of the vaccine. Research has shown that receiving the HPV vaccine at the recommended ages can provide the best immune response, offering long-lasting protection against several types of HPV infections that can lead to various cancers.
Hpv Prevention Strategies For Adolescents
Adolescence is a crucial time in a person’s life when they experience significant physical, emotional, and social changes. It is during this stage that teenagers become more independent and start making decisions that can impact their health in the long run. One important health concern among adolescents is the prevention of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various forms of cancer, including cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers. Implementing effective HPV prevention strategies for adolescents is vital to protect their future health.
One of the key strategies for HPV prevention among adolescents is vaccination. Vaccines are considered a powerful tool in the fight against HPV infection and its associated health risks. The HPV vaccine is designed to protect against the most common types of HPV that cause cancer and genital warts. Vaccination can be administered to both males and females, typically between the ages of 11 and 12, before they become sexually active. The vaccine is most effective when given before any exposure to the virus occurs. Therefore, early vaccination is essential in preventing HPV infection and its potential consequences.
In addition to vaccination, promoting safe sex practices is another critical strategy for HPV prevention among adolescents. Encouraging the consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual intercourse can help reduce the risk of HPV transmission. It is important for adolescents to understand the importance of using condoms as a protective measure, even if they have already received the HPV vaccine. Emphasizing the importance of open communication with sexual partners regarding sexual history and testing for sexually transmitted infections is also crucial for preventing the spread of HPV.
- Regular screening is another vital aspect of HPV prevention among adolescents. Screening tests, such as Pap smears and HPV tests, can detect early signs of HPV infection and precancerous cell changes. Regular screening allows for early detection and timely intervention, reducing the risk of developing HPV-related cancers. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating adolescents about the importance of regular screening and ensuring they have access to these tests.
| HPV Prevention Strategies for Adolescents |
|---|
| Vaccination |
| Safe sex practices |
| Regular screening |
Safe Sex Practices To Reduce Hpv Transmission
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) worldwide. It is a group of more than 200 related viruses, and some of them can lead to serious health problems including cervical, anal, penile, vaginal, and oropharyngeal cancers. While HPV can be transmitted through various forms of sexual contact, practicing safe sex can greatly reduce the risk of transmission. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of safe sex practices in relation to HPV prevention.
One of the key safe sex practices to reduce the transmission of HPV is consistent and correct use of condoms. Condoms act as a barrier and can help prevent the exchange of bodily fluids, including HPV, during sexual intercourse. It is important to use condoms from the beginning to the end of any sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Another essential safe sex practice is regular sexual health check-ups. Getting tested for STIs, including HPV, on a regular basis allows for early detection and treatment. This not only helps to protect oneself but also reduces the risk of transmitting HPV to sexual partners. Regular check-ups can also identify any signs or symptoms of HPV-related cancers, ensuring timely medical intervention and effective management.
- Using condoms: Condoms act as a barrier and can help prevent the exchange of bodily fluids, including HPV, during sexual intercourse. It is important to use condoms from the beginning to the end of any sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- Regular sexual health check-ups: Getting tested for STIs, including HPV, on a regular basis allows for early detection and treatment. This not only helps to protect oneself but also reduces the risk of transmitting HPV to sexual partners. Regular check-ups can also identify any signs or symptoms of HPV-related cancers, ensuring timely medical intervention and effective management.
| Safe Sex Practices to Reduce HPV Transmission |
|---|
| Using condoms |
| Regular sexual health check-ups |
| Consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual activity |
| Getting tested for STIs, including HPV, on a regular basis |
Regular Screening For Hpv-Related Cancers
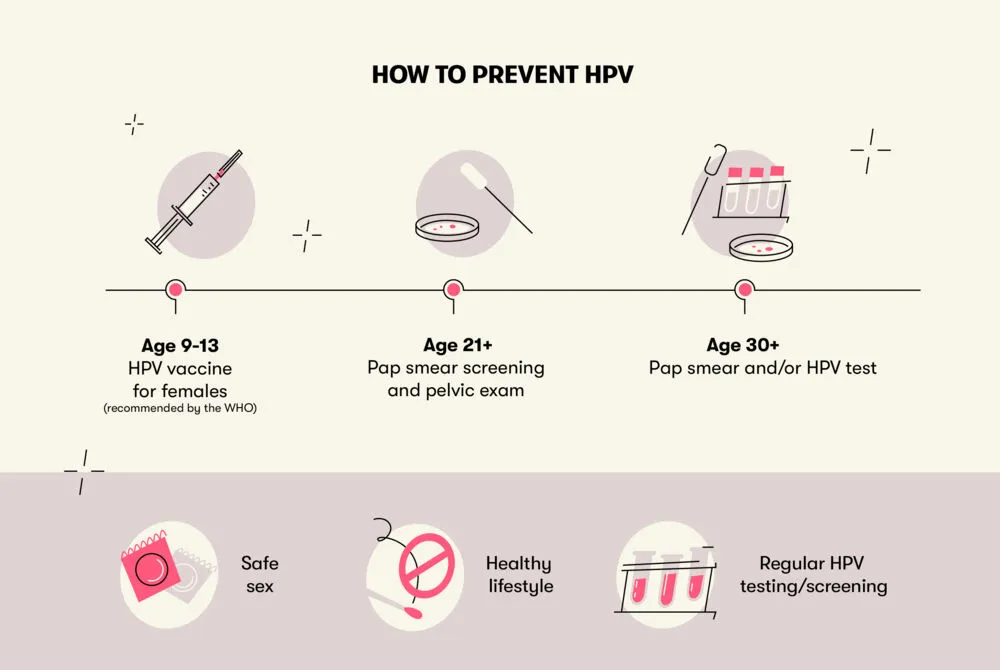
Regular screening plays a crucial role in the prevention and early detection of HPV-related cancers. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various types of cancers, including cervical, vaginal, vulvar, anal, penile, and oropharyngeal cancers. By undergoing regular screenings, individuals can identify any abnormal changes in their cells before they progress into cancerous conditions. This blog post will highlight the importance of regular screening for HPV-related cancers and discuss the recommended screening methods.
- Why is regular screening important?
Regular screening is essential because it allows for the early detection of abnormal cell changes caused by HPV. The majority of HPV infections are asymptomatic, meaning individuals do not experience any noticeable symptoms. Therefore, regular screening is necessary to identify any potential precancerous or cancerous conditions. Early detection increases the likelihood of successful treatment and significantly reduces the morbidity and mortality rates associated with HPV-related cancers.
- Recommended screening methods
There are several screening methods available for the detection of HPV-related cancers. The most common screening test for cervical cancer is the Pap smear or Pap test. It involves collecting a sample of cells from the cervix and examining them under a microscope for any abnormalities. Another screening method is the HPV DNA test, which identifies the presence of high-risk HPV strains in cervical cells. This test can be used as a primary screening tool or in conjunction with the Pap smear. For other HPV-related cancers, such as anal, penile, and oropharyngeal cancers, there are no routine screening tests available. However, individuals with specific risk factors or symptoms should consult their healthcare providers for further evaluation and screening recommendations.
- Frequency of screenings
The frequency of screenings for HPV-related cancers varies depending on several factors, including age, gender, and individual risk factors. For cervical cancer, most guidelines recommend starting regular screenings at the age of 21 and continuing every three to five years. However, if both the Pap smear and HPV DNA test are used together (co-testing), screening intervals may be extended to every five years for individuals aged 30 and above. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening schedule based on individual factors and recommendations.
regular screening for HPV-related cancers is highly important for the early detection and prevention of these potentially life-threatening conditions. By undergoing recommended screening methods at the recommended frequency, individuals can identify any abnormal cell changes caused by HPV and receive timely interventions and treatments. Regular screening, combined with HPV vaccination and practicing safe sex, is vital for comprehensive HPV prevention strategies.
Promoting Awareness And Education On Hpv Prevention
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to significant health problems, including various types of cancer. In order to combat the spread of HPV and reduce the associated risks, it is crucial to promote awareness and education on HPV prevention. By increasing knowledge about HPV, its transmission, and available preventive measures, individuals can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to protect their health.
One approach to promoting awareness and education on HPV prevention is through comprehensive sex education programs. These programs provide adolescents and young adults with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health, including HPV. By teaching them about the risks of HPV infection and the importance of preventive measures, such as vaccination and safe sex practices, these programs empower individuals to make informed choices and protect themselves against HPV-related diseases.
In addition to sex education programs, it is vital to utilize various communication channels to disseminate information about HPV prevention. This can include online platforms, social media campaigns, and educational materials distributed in healthcare settings, schools, and community centers. By leveraging these channels, we can reach a wider audience and ensure that accurate and up-to-date information on HPV prevention is accessible to all.
Furthermore, healthcare providers play a critical role in promoting awareness and education on HPV prevention. They have the opportunity to educate their patients about HPV, recommend vaccination, and provide guidance on safe sex practices and regular screening. By incorporating HPV prevention into routine healthcare visits, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall efforts in preventing HPV-related diseases and improving public health outcomes.
- In conclusion, promoting awareness and education on HPV prevention is of utmost importance in reducing the burden of HPV-related diseases. By implementing comprehensive sex education programs, utilizing various communication channels, and involving healthcare providers, we can empower individuals to take proactive steps in protecting their health. Together, let’s work towards a future where HPV prevention is a priority and the incidence of HPV-related diseases is significantly reduced.
| References |
|---|
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). HPV and Cancer. |
| World Health Organization. (2017). Human papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical cancer. |
The Role Of Healthcare Providers In Hpv Prevention
When it comes to preventing Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its associated diseases, healthcare providers play a crucial role. They are at the forefront of providing education, awareness, and interventions to individuals of all ages. Healthcare providers have the responsibility of advocating for HPV prevention, offering vaccination services, conducting screenings, and promoting safe sex practices. Through their expertise and guidance, they can effectively contribute to reducing the incidences and burden of HPV-related diseases.
Healthcare providers are instrumental in advocating for HPV prevention by raising awareness about the importance of vaccination and its benefits. Educating patients and the general public about the risks of HPV infection and the available preventive measures can lead to increased uptake of vaccination. Providers can disseminate information about the safety, efficacy, and accessibility of HPV vaccines to dispel misconceptions and address concerns. By actively engaging in conversations regarding HPV prevention, healthcare providers can empower individuals to make informed decisions and take charge of their sexual health.
Furthermore, healthcare providers are well-positioned to offer HPV vaccination services to eligible individuals. They can assess the vaccine eligibility criteria, provide information about the appropriate HPV vaccine types available, and administer the vaccines. This proactive approach ensures that individuals receive the necessary protection against high-risk HPV strains. As trusted healthcare professionals, providers can address concerns related to vaccine safety and side effects, ultimately promoting the acceptance and uptake of HPV vaccination in their communities.
In addition to vaccination, healthcare providers play a pivotal role in conducting regular screenings for HPV-related cancers. They can advise individuals on the importance of routine screenings and early detection, as well as provide guidance on the recommended screening intervals. By emphasizing the significance of regular screenings, healthcare providers can contribute to the timely identification and management of HPV-related infections and potential cancerous changes. Through these efforts, they actively participate in the prevention and control of HPV-related diseases.
Healthcare providers also have the responsibility of promoting safe sex practices as a fundamental component of HPV prevention. They can advocate for condom use, discuss the importance of mutual monogamy and reducing the number of sexual partners, and provide counseling on sexual health. By addressing risk factors associated with HPV transmission, healthcare providers empower individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual behaviors and reduce their likelihood of acquiring or transmitting HPV infections.
healthcare providers have a fundamental role to play in HPV prevention. Their advocacy, provision of vaccination services, conduct of screenings, and promotion of safe sex practices contribute significantly to reducing the burden of HPV-related diseases. By actively engaging with patients and communities, healthcare providers can be instrumental in increasing awareness, encouraging preventive behaviors, and ultimately securing the future health of individuals at risk of HPV infection.
Supporting Hpv Prevention Efforts Through Policy
In order to effectively combat the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), it is crucial to implement comprehensive prevention strategies. While vaccination and safe sex practices play a significant role in reducing the transmission of HPV, the implementation of supportive policies is equally important. Policies can create a conducive environment for prevention efforts and help ensure their long-term success. This article highlights the significance of supporting HPV prevention through policy and explores various strategies that can be adopted.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| The impact of policy in HPV prevention |
| Policy strategies for HPV prevention |
| The role of healthcare providers in policy implementation |
The impact of policy in HPV prevention
When it comes to tackling public health issues like HPV, policies play a crucial role in shaping prevention efforts. National and regional policies can provide the necessary framework to prioritize and allocate resources for HPV prevention initiatives. These policies may focus on various aspects, including the promotion of vaccination, the establishment of screening guidelines, and the integration of HPV education into school curricula. By supporting and implementing policies, governments can demonstrate their commitment to combatting HPV and preventing associated diseases.
Policy strategies for HPV prevention
There are several key policy strategies that can support HPV prevention efforts. Firstly, policymakers can prioritize the inclusion of HPV vaccines in routine immunization schedules, making them more accessible to adolescents. Secondly, policies can be formulated to improve public awareness and education about HPV, its transmission, and prevention methods. This can include awareness campaigns in schools, colleges, and communities. policymakers can collaborate with healthcare organizations to devise screening guidelines and ensure regular screenings for HPV-related cancers.
The role of healthcare providers in policy implementation
Healthcare providers play a vital role in the successful implementation of HPV prevention policies. They can actively participate in policy development by providing insights and recommendations based on their expertise. Healthcare providers can also engage in community outreach programs to raise awareness about the importance of HPV prevention. By incorporating policy guidelines into their clinical practice, healthcare providers can ensure that vaccination, screenings, and education are seamlessly integrated into patient care. They can also contribute to ongoing research and evaluation of policy effectiveness in HPV prevention.